This tutorial explaines how to intitialize an audformat database object from a data collection that's store in a pandas dataframe.
You can also find an official example using emo db here
First you would need the neccessary imports:
import os # file operations
import pandas as pd # work with tables
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 10)
import audformat.define as define # some definitions
import audformat.utils as utils # util functions
import audformat
import pickleWe load a sample pandas dataframe from a speech collection labeled with age and gender.
df = pickle.load(open('../files/sample_df.pkl', 'rb'))
df.head(1)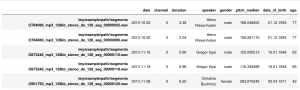
We can then construct an audformat Databse object from this data like this
# remove the absolute path to the audio samples
root = '/my/example/path/'
files = [file.replace(root, '') for file in df.index.get_level_values('file')]
# start with a general description
db = audformat.Database(
name='age-gender-samples',
source='intern',
usage=audformat.define.Usage.RESEARCH,
languages=[audformat.utils.map_language('de')],
description=(
'Short snippets annotated by '
'speaker and speaker age and gender.'
),
)
# add audio format information
db.media['microphone'] = audformat.Media(
type=audformat.define.MediaType.AUDIO,
sampling_rate=16000,
channels=1,
format='wav',
)
# Describe the age data
db.schemes['age'] = audformat.Scheme(
dtype=audformat.define.DataType.INTEGER,
minimum=0,
maximum=100,
description='Speaker age in years',
)
# describe the gender data
db.schemes['gender'] = audformat.Scheme(
labels=[
audformat.define.Gender.FEMALE,
audformat.define.Gender.MALE,
],
description='Speaker sex',
)
# describe the speaker id data
db.schemes['speaker'] = audformat.Scheme(
dtype=audformat.define.DataType.STRING,
description='Name of the speaker',
)
# initialize a data table with an index which corresponds to the file names
db['files'] = audformat.Table(
audformat.filewise_index(files),
media_id='microphone',
)
# now add columns to the table for each data item of interest (age, gender and speaker id)
db['files']['age'] = audformat.Column(scheme_id='age')
db['files']['age'].set(df['age'])
db['files']['gender'] = audformat.Column(scheme_id='gender')
db['files']['gender'].set(df['gender'])
db['files']['speaker'] = audformat.Column(scheme_id='speaker')
db['files']['speaker'].set(df['speaker'])and finally inspect the result
db
name: age-gender-sample
description: Short snippets annotated by speaker and speaker age and gender.
source: intern
usage: research
languages: [deu]
media:
microphone: {type: audio, format: wav, channels: 1, sampling_rate: 16000}
schemes:
age: {description: Speaker age in years, dtype: int, minimum: 0, maximum: 100}
gender:
description: Speaker sex
dtype: str
labels: [female, male]
speaker: {description: Name of the speaker, dtype: str}
tables:
files:
type: filewise
media_id: microphone
columns:
age: {scheme_id: age}
gender: {scheme_id: gender}
speaker: {scheme_id: speaker
}and perhaps as a test get the unique valuesof all speakers:
db.tables['files'].df.speaker.unique()Important: note that the path to the audiofiles needs to be relative to where the database.yaml file resides and is not allowed to start with "./", so if you do
db.files[0]this should result in something like
audio/mywav_0001.wav